How to Source Beauty Tools from China Like a Pro
December 1, 2025
Understanding The Rise of AI and Automation in China’s Trading Sector
December 8, 2025Key Highlights
Here is a quick overview of what you will learn about making custom products in China:
- China offers two main manufacturing models: OEM, where you provide the design, and ODM, where you customize a factory’s existing product.
- Thorough research and clear product specifications are crucial before you contact any Chinese manufacturer.
- Protecting your intellectual property with trademarks and NNN agreements is a non-negotiable step.
- Effective quality control throughout the product development and production stages ensures your final items meet standards.
- A well-managed supply chain, from sourcing to shipping, is key to success.
Introduction
Have you ever had a unique product idea but weren’t sure how to bring it to life? Custom product manufacturing in China could be your answer. Leveraging China sourcing allows you to turn your vision into a tangible final product, often at a competitive price. This guide is designed for beginners, providing you with essential tips and a step-by-step process. We will explore everything from understanding the basics to navigating challenges, ensuring you are well-equipped for your manufacturing journey.
Understanding Custom Product Manufacturing in China
Diving into custom manufacturing in China might seem complex, but it’s a well-established process. It involves partnering with Chinese factories to produce goods based on your specific designs and requirements. Understanding this landscape is the first step toward achieving the desired quality of products for your business.
From selecting the right product type to managing your supply chain, every detail matters. Whether you work directly with a factory or use a sourcing agent, knowing the fundamentals will help you make informed decisions. Let’s break down what custom manufacturing entails and why China is a global hub for it.
What Is Custom Manufacturing?
Custom manufacturing, at its core, is a production process where goods are created according to a customer’s precise specifications. Instead of buying off-the-shelf items, you get to define everything from the materials and dimensions to the branding and packaging. This approach is ideal when you need a product tailored to your unique vision or market niche.
The journey begins with your product design. This initial phase is critical, as it lays the groundwork for the entire production process. You provide the factory with your detailed plans, and they use their equipment and expertise to create your item. This collaboration ensures that the final product aligns perfectly with your expectations.
Whether you are creating a new gadget, a piece of apparel, or a specialized component, custom production offers unparalleled control. It allows you to create something truly unique for your product category, setting your brand apart from the competition and ensuring the final result is exactly what you envisioned.
Why Choose China for Custom Manufacturing?
For decades, China has been a top choice for manufacturing, and for good reason. The country’s primary advantage is its ability to produce goods at a low cost. This is largely due to a vast labor force and established supply chains for raw materials, which translate into competitive prices for businesses looking to produce large orders.
Beyond cost, Chinese manufacturers possess an incredible production capacity. Factories are often equipped with advanced technology capable of handling high-volume orders with impressive speed and efficiency. This ability to scale means you can go from a small batch to mass production without needing to switch suppliers.
This combination of low manufacturing costs and high production capacity makes China a great place for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re a startup or an established brand, you can find a Chinese manufacturer that can meet your needs, helping you bring your custom product to market efficiently and affordably.
Key Industries for Custom Manufacturing in China

Many businesses turn to China for its expertise in several key sectors. These industries have well-developed ecosystems, from raw material suppliers to specialized factories, ensuring a smooth production process. This makes it easier to find reliable partners for your project.
Some of the most common industries for custom manufacturing include:
- Electronics: From consumer gadgets to complex components.
- Textiles and Apparel: Clothing, accessories, and home textiles.
- Plastics and Molding: Custom plastic parts, enclosures, and toys.
- Metals and Hardware: Stamped metal parts, die-casting, and tools.
- Personal Care :Cosmetics ,Skincare, Haircare , bodycare products and tools
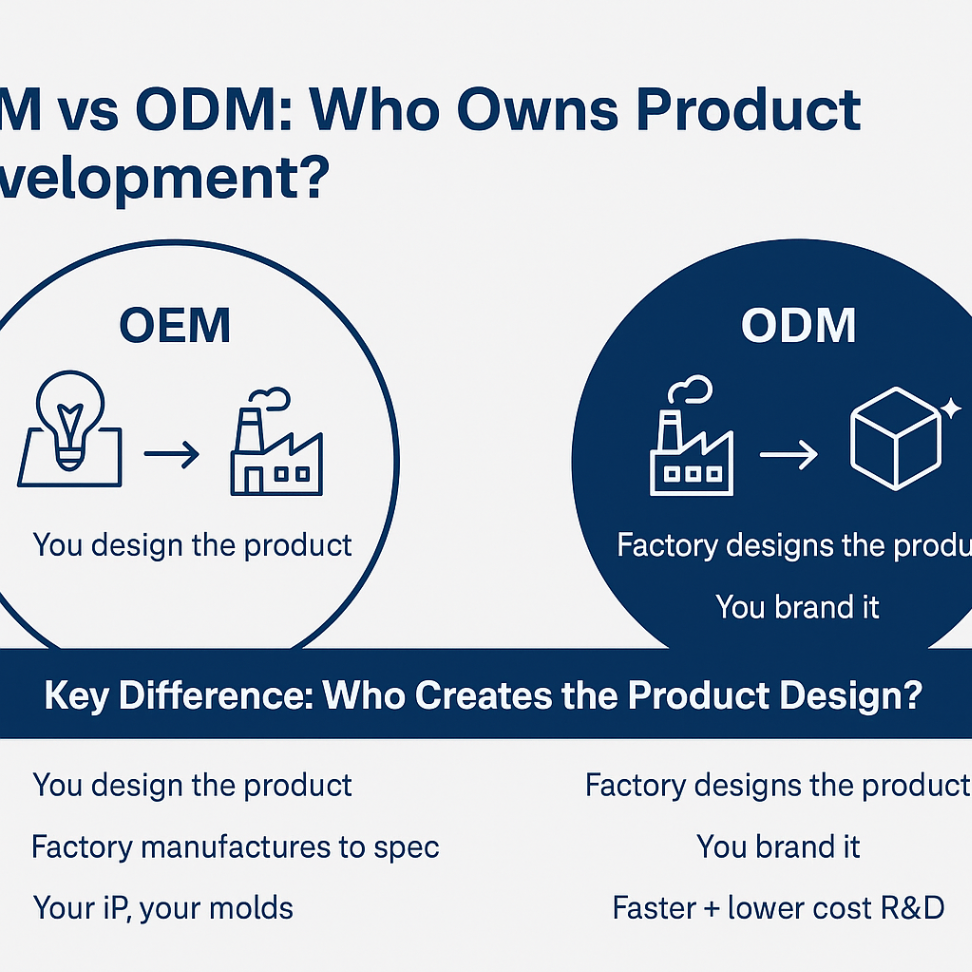
Types of Custom Manufacturing: OEM vs ODM
When you decide to manufacture a custom product, you’ll encounter two primary models: Original Equipment Manufacturing (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturing (ODM). Understanding the difference between them is vital for your product development strategy and will influence your entire production journey.
Choosing between OEM and ODM determines the level of your involvement in design, tooling, and overall investment. Finding the best way forward depends on your budget, timeline, and how unique you want your product to be before starting mass production. Let’s explore what each model means for your business.
What Does OEM Mean in China?
OEM, or Original Equipment Manufacturing, is a model where a factory produces goods based on your exclusive design and product specifications. In this scenario, you are responsible for the research, development, and design of the product. You provide the manufacturer with detailed plans, and they act as your production partner to bring your vision to life.
This approach gives you complete control over the final product. It’s the preferred path for businesses with a unique invention or those wanting to create a product that is entirely their own. The production process is tailored to your exact needs, from materials to functionality, allowing for a high degree of customization.
For businesses that want to sell items under a private label in China and have already invested in product design, OEM is an excellent choice. It ensures your intellectual property remains yours while leveraging the manufacturing expertise and cost-effectiveness of a Chinese factory.
What Does ODM Mean in China?
ODM, or Original Design Manufacturing, offers a different path to creating new products. In this model, the manufacturer already has existing product designs and tooling. You can select a product from their catalog and request modifications, such as changing colors, adding your logo, or making minor functional tweaks.
This is a fantastic option for businesses that want to get to market quickly without investing heavily in research and product design. The service providers have already done the hard work of developing a market-tested product, which significantly reduces your development time and costs.
Essentially, you are branding an existing product as your own. Many startups and small businesses find the ODM model appealing because it lowers the barrier to entry. It allows them to launch new products with minimal risk and upfront investment, making it a popular choice for a wide range of consumer goods.
Differences Between OEM and ODM Models
The core difference between OEM and ODM lies in who owns the product design and handles the product development. With OEM, you own the intellectual property and provide the full design. With ODM, the factory owns the base design, and you customize it. This distinction has a major impact on production costs and time to market.
Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right partner and strategy. OEM requires more upfront investment in R&D, while ODM allows for a faster launch with lower costs. Your choice will also affect long-term factors like product quality control and supplier exclusivity.
Here is a simple breakdown of the main differences:
| Feature | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Ownership | You (the buyer) own the design and IP. | The manufacturer owns the base design. |
| Development | You are responsible for all R&D and design. | The manufacturer handles most of the R&D. |
| Upfront Costs | Higher due to R&D, tooling, and molds. | Lower, as tooling often already exists. |
| Time to Market | Longer, due to the full development cycle. | Faster, as you start with an existing product. |
| Uniqueness | High. The product is exclusively yours. | Low. Similar products may be sold by others. |
Which Option Is Best for Your Business?
Deciding between OEM and ODM depends entirely on your business goals, resources, and product strategy. Do you have a groundbreaking idea and the budget for development? Or are you looking to quickly expand your product range with proven items? Answering these questions will point you in the right direction.
If you have a unique design and detailed product specifications, OEM is the way to go. This model gives you full control and ensures your product is exclusive to your brand. It’s ideal for companies that want to build a strong brand identity around innovative products and can manage a more complex supply chain.
On the other hand, if you’re a startup or a small business with a limited budget, ODM is often the more practical choice. It allows you to enter the market quickly with a private label in China, leveraging the manufacturer’s existing production capacity and designs. This model minimizes risk and upfront costs, making it a great starting point.
Benefits of Manufacturing Custom Products in China
Why do so many businesses choose to manufacture custom products in China? The advantages are significant, extending far beyond just the final price tag. China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers a powerful combination of efficiency, scale, and expertise that is hard to match anywhere else in the world. From mass production capabilities to a robust supply chain, the benefits can give your business a serious competitive edge.
Partnering with a Chinese manufacturer allows you to tap into a system designed for high-volume output while maintaining quality standards. The low cost and impressive production capacity create opportunities that can help your business grow and innovate. Let’s explore these benefits in more detail.
Cost Efficiency and Scale
One of the most compelling reasons to manufacture in China is the remarkable cost efficiency. Lower labor wages and affordable raw materials significantly reduce overall production costs, especially when compared to manufacturing in Western countries. This cost advantage allows you to offer your products at competitive prices while maintaining healthy profit margins.
This cost-effectiveness is amplified by the potential for mass production. Chinese factories are built to handle large order volumes, which creates economies of scale. As your order quantity increases, the per-unit cost typically decreases, making it highly economical to scale your business. This is a huge advantage for companies planning for growth.
Ultimately, the ability to achieve low-cost production without sacrificing the potential for large-scale output is a powerful combination. It enables businesses, from startups to large corporations, to manage their budgets effectively and compete on price in the global marketplace.
Wide Range of Suppliers
China’s manufacturing landscape is incredibly vast and diverse. You can find a Chinese manufacturer for almost any product imaginable, creating a competitive environment that benefits you as a buyer. This wide selection means you can find a factory that perfectly matches your needs in terms of specialization, quality, and price.
The sourcing process to find these suppliers has become easier over the years. You have many different ways to connect with potential partners, whether you’re searching from your office or traveling to China. This accessibility simplifies the initial steps of setting up your supply chain.
Here are a few popular methods for finding suppliers:
- Online B2B Platforms: Websites like Alibaba and Made-in-China host millions of supplier profiles.
- Trade Shows: Events like the Canton Fair offer opportunities to meet manufacturers in person.
- Sourcing Service Providers: This is the best approach to connect with suppliers and import from China.Agents can connect you with vetted factories that fit your requirements.
Advanced Production Capabilities
Over the past few decades, Chinese factories have undergone a massive technological transformation. Many now boast state-of-the-art machinery and advanced production techniques that rival those found anywhere in the world. This evolution means you can achieve high standards of precision and quality for your custom products.
These advanced capabilities also contribute to an impressive production capacity. Factories are designed for efficiency, allowing them to handle large orders and complete them within tight deadlines. This quick turnover is a significant advantage for businesses that need to get their products to market swiftly.
Whether your project requires complex plastic injection molding, precision metal stamping, or intricate electronics assembly, you can find Chinese factories with the right technology. The continuous investment in modernizing the production process ensures that manufacturers can meet the ever-increasing demands for quality and complexity from global clients.
Opportunities for Product Innovation
Working with experienced Chinese manufacturers can be a catalyst for product innovation. Many factories have spent years, or even decades, producing items in a specific niche. This deep expertise can be an invaluable resource as you go through the product development phase, helping you refine your product design and avoid common pitfalls.
Don’t be afraid to collaborate with your supplier. They may have suggestions for improving your design for manufacturing, using alternative materials to lower costs, or adding new features you hadn’t considered. This partnership can elevate your idea from a simple concept to a market-ready final product.
By leveraging the manufacturer’s experience, you can create new products that are not only well-designed but also optimized for production. This collaborative approach can lead to a better, more innovative final product, giving you a competitive edge and helping you meet the evolving needs of your customers.
Common Challenges in Custom Manufacturing in China
While manufacturing in China offers many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Being aware of potential hurdles is the first step to overcoming them. Beginners, in particular, may face issues ranging from a language barrier to difficulties with quality control, which can lead to poor quality products if not managed correctly.
Protecting your intellectual property and navigating requirements like Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are other common concerns. A misstep in any of these areas can disrupt your supply chain and cost you a lot of time and money. Let’s look at these challenges and how to address them proactively.
Language and Communication Barriers
One of the most immediate challenges you’ll face is the language barrier. While many sales representatives at Chinese factories speak some English, nuances and technical details can easily get lost in translation. Misunderstandings can lead to production errors, delays, and frustration on both sides.
Achieving clear communication is essential for a successful project. It’s crucial to be as precise and unambiguous as possible in all your interactions. Using simple language, visual aids, and written confirmations can help bridge the gap and ensure everyone is on the same page.
Here are some tips for better communication:
- Hire a Sourcing Agent: A bilingual professional can ensure your requirements are perfectly understood.
- Use Written Communication: Document everything in emails so you have a clear record of all discussions and agreements.
- Utilize Communication Tools: Platforms like WeChat are popular for quick updates, but use them alongside formal channels like email.
Quality Control Issues
Ensuring consistent product quality is one of the biggest concerns when manufacturing overseas. Without a proper system in place, you risk receiving a shipment of goods that don’t meet your quality standards. This is why establishing robust quality control procedures from the very beginning is non-negotiable.
Your quality expectations must be clearly communicated to the factory before the production process begins. This includes providing detailed specifications, approved samples, and a list of acceptable and unacceptable defects. Never assume the factory’s idea of “good quality” matches yours.
To effectively manage product quality, you should plan for inspections at different stages of production. This could include checking raw materials, inspecting items mid-production, and conducting a final inspection before the order ships. Many businesses hire sourcing companies in China to perform these checks on their behalf, ensuring an unbiased assessment.
Intellectual Property Protection Concerns
The fear of having a unique product idea or design stolen is a valid concern for anyone manufacturing in China. Intellectual property (IP) theft can happen, but you can take proactive steps to protect yourself. The key is to understand that IP laws in China work differently than in Western countries.
Safeguarding product designs starts with legally protecting them in China itself. This means registering your trademarks and patents with the appropriate Chinese authorities before you even start talking to factories. China operates on a “first-to-file” system, so whoever registers the IP first owns it in that country, regardless of who invented it.
In addition to legal registrations, you should use strong contracts. A well-drafted agreement that clearly outlines your product specifications and IP ownership is essential. Many experts recommend using an “NNN” (Non-Disclosure, Non-Use, Non-Circumvention) agreement, which is specifically designed for the Chinese legal system and offers stronger protection than a standard Western NDA.
Navigating Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
When you start contacting factories, you’ll quickly encounter the term Minimum Order Quantity, or MOQ. This is the fewest number of units a manufacturer is willing to produce in a single production run. Factories have MOQs to cover their production costs and ensure the job is profitable for them.
For startups and small businesses, MOQs can be a significant hurdle, as they often require a large upfront investment. The MOQ can vary widely depending on the product type and the factory. A simple product made from common materials might have a lower MOQ, while a complex item requiring custom components will likely have a higher one.A sourcing company can help to navigate MOQ issues , as they are already working with reputed factories from long time and have completed multiple projects which makes factories believe them as a consistent and repeated buyer.
While MOQs can seem rigid, there is sometimes room for negotiation.
- Negotiate a Higher Price: Some factories may agree to produce smaller orders if you’re willing to pay a higher price per unit.
- Ask About Stock Materials: If the factory can use materials they already have in stock, they may be more flexible on the MOQ.
Essential Preparations Before You Start
Jumping into manufacturing without proper preparation is a recipe for disaster. Before you contact a single Chinese manufacturer, you need to do your homework. This means getting your ideas out of your head and into a concrete plan. A solid foundation will make the entire production process smoother and more successful.
From creating detailed product specifications to setting a realistic budget and timeline, these preparatory steps are crucial. They ensure that you and your potential sourcing agent or factory are speaking the same language from day one. Let’s cover the essential preparations you need to make.
Defining Your Product Specifications
Before a factory can give you an accurate quote, they need to know exactly what you want them to make. This is where a detailed product specification sheet, or “spec sheet,” comes in. This document outlines every single detail of your product and serves as the blueprint for manufacturing.
Your spec sheet should leave no room for interpretation. The more detailed it is, the lower the risk of misunderstandings and production errors. It should cover all physical attributes, materials, colors, branding, and packaging requirements for your specific product type.
A comprehensive spec sheet should include:
- Dimensions and Weight: Provide precise measurements for the product and any packaging.
- Materials and Colors: Specify the exact materials to be used and include Pantone color codes.
- Functionality and Performance: Describe how the product should work and any quality standards it must meet.
Setting Your Budget and Timeline
Knowing your numbers is critical before you begin. You need a realistic budget that covers more than just the per-unit production costs. Your total landed cost will include expenses like tooling and molds, shipping, import tariffs, and quality inspections. Forgetting these additional costs can quickly derail your project.
Start by researching each potential expense to build a comprehensive budget. This will help you determine a viable price point for your product and understand your potential profit margins. Having a clear budget also empowers you during negotiations with suppliers.
Equally important is setting a realistic timeline. The manufacturing process takes time, from finding a supplier and prototyping to mass production and shipping. Factor in potential delays, such as holidays like Chinese New Year when factories shut down. A well-planned timeline helps you manage expectations and coordinate your product launch effectively.
Preparing Design Files and Prototypes
A great idea is just the beginning; you need to translate it into a format that a manufacturer can understand. Professional product design files are essential for this. For most products, this means creating 2D technical drawings and 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files that detail every dimension, part, and assembly.
These design files are the universal language of manufacturing. They eliminate ambiguity and ensure the factory knows exactly how to build your product. If design isn’t your strong suit, it’s wise to hire a professional product designer or engineer to create these files for you.
Once your design files are ready, the next step is creating a prototype. A physical sample allows you to test the product’s form, fit, and function before committing to mass production. This is your chance to catch flaws and make refinements, saving you from costly mistakes down the road. Never skip the prototype stage in your product development process.
Understanding Chinese Business Culture
Doing business in China involves navigating a cultural landscape that can be quite different from the West. Understanding and respecting Chinese business culture can significantly improve your relationships with suppliers and lead to better outcomes in your sourcing process. Building trust and rapport is highly valued.
One key concept is “guanxi,” which translates to relationships or connections. Chinese manufacturers often prefer to do business with people they know and trust. Investing time in building a personal connection, even through informal chats, can go a long way.
Patience is also a virtue in negotiations. The process may be slower and more relationship-focused than you’re used to. It’s important to remain calm, polite, and respectful, even during disagreements. Taking the time to understand their perspective will help you build a stronger, more collaborative partnership and improve your overall supply chain management.
What You Need to Get Started with Custom Manufacturing
Are you ready to take the next step? Getting started with custom manufacturing requires a few key resources and a clear plan of action. You need to know where to find reliable partners, how to develop your product, and what legal steps to take to protect your business.
Whether you choose to work with a sourcing agent or directly with factories, having the right tools and knowledge is essential. This section will outline the practical things you need to begin your China sourcing journey, from finding suppliers to ensuring you can communicate effectively.
Finding Reliable Suppliers
The success of your project hinges on finding a reliable supplier. A good partner will deliver quality products on time and communicate clearly, while a bad one can cause endless headaches. Your first task is to conduct thorough research and due diligence to create a shortlist of potential manufacturers.
Don’t just choose the supplier with the lowest price. Look for manufacturers with good reviews, relevant experience in your product category, and proper certifications. Checking for negative reviews or complaints can be just as insightful as reading positive ones.
Here are some effective ways to find reliable suppliers:
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Alibaba allow you to search for suppliers, but always verify their credentials.
- Industry Trade Shows: Events like the Canton Fair are great for meeting suppliers face-to-face.
- Using a Sourcing Agent: An agent on the ground in China can vet factories for you, saving you time and reducing risk.
Resources for Product Design and Development
If you have a product idea but lack the technical skills to create professional design files, don’t worry. There are numerous resources available to help you with product design and development. These service providers can turn your concept into detailed plans ready for manufacturing.
You can hire freelance product designers or engineering firms through online platforms like Upwork or by searching for specialized agencies. These experts can create the necessary CAD files and technical drawings, ensuring your vision is communicated accurately to the factory.
Alternatively, if you opt for an ODM model, the manufacturer itself can be a resource. Their in-house design team has already developed a range of products. You can work with them to make modifications and prepare the final product for your brand, streamlining the development process significantly.
Legal and Compliance Requirements
Navigating the legal and compliance landscape is a critical part of manufacturing. You need to ensure your business and your product are protected. This starts with having strong contracts with your supplier that clearly outline payment terms, quality standards, and ownership of intellectual property.
Before you begin, you must also protect your IP by registering trademarks and patents in China. As mentioned earlier, this is a crucial step to prevent others from copying your brand or product design. Consulting with a lawyer who specializes in Chinese IP law is highly recommended.
Finally, your product must meet the safety and compliance standards of the country where you plan to sell it. For example, electronics sold in the United States need FCC certification, while products for Europe may require a CE mark. It’s your responsibility to know these legal requirements and ensure your product specifications and testing procedures meet them.
Tools for Effective Communication
Clear communication is the backbone of a successful manufacturing partnership. Thankfully, modern technology offers plenty of tools to help you stay connected with your Chinese suppliers, even from thousands of miles away. Choosing the right tools can make the negotiation and production process much smoother.
While email is essential for formal documentation and sharing detailed files, instant messaging apps are invaluable for quick questions and updates. Most Chinese business professionals use WeChat as their primary communication tool. Downloading and using it can significantly speed up day-to-day interactions.
Here are some essential communication tools:
- WeChat: Use this for daily communication, sharing photos of production progress, and building rapport.
- Email: Reserve this for official communication, such as placing orders, confirming specifications, and discussing payment terms.
For complex discussions or when language is a major barrier, consider hiring a sourcing agent or a translator to facilitate communication.
Step-by-Step Guide to Custom Product Manufacturing in China
Now that you understand the basics, let’s walk through the entire process from start to finish. This step-by-step guide will provide a clear roadmap for your custom manufacturing journey in China. Following these steps in order will help you stay organized and avoid common pitfalls along the way.
From initial research and product design to final delivery, each step is a building block for the next. Whether you’re working with a sourcing agent or directly with service providers, this structured approach will help you manage the production process effectively.
Step 1: Research and Shortlist Potential Manufacturers
The first step in your journey is to find potential manufacturing partners. This research phase is crucial for identifying companies that have the right experience and capabilities for your project. Cast a wide net initially to gather a good number of options before narrowing them down.
Use a combination of methods to find suppliers. Online B2B platforms are a great starting point, but don’t stop there. Attending trade fairs or searching industry-specific directories can uncover hidden gems that may not have a strong online presence. The goal is to build a long list of potential Chinese manufacturer candidates.
Once you have your list, begin the due diligence process to create a shortlist.
- Review Company Profiles: Look for manufacturers that specialize in your product type and have several years of experience.
- Check for Certifications: Verify if they have quality management certifications like ISO 9001.
Step 2: Contact Suppliers and Request Quotes
With your shortlist in hand, it’s time to make initial contact and request quotes. How you approach this step says a lot about you as a potential client. A professional and detailed inquiry is more likely to get a serious response than a vague, one-line message.
Prepare a formal Request for Quotation (RFQ) document. This should include your detailed product specifications, design files, desired order quantity, and target price. The more information you provide, the more accurate the quotes will be. This saves a lot of time and back-and-forth communication.
Send your RFQ to at least 3-5 suppliers on your shortlist. This will allow you to compare production costs and see what a reasonable price range is for your product. Don’t automatically go for the lowest price; consider the supplier’s responsiveness, communication skills, and willingness to answer your questions as part of your evaluation.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Credentials and Capabilities
After receiving quotes, you need to dig deeper and verify that the most promising suppliers are legitimate and capable. This due diligence step is vital to avoid scams and ensure you partner with a reliable supplier that can meet your quality standards. Never take a supplier’s claims at face value.
Ask for copies of their business license and any quality certifications they claim to have. You can use third-party services to verify these documents. It’s also a good idea to ask for references from past clients, preferably from your own country, so you can get firsthand feedback on their performance.
Evaluate their production capacity and years of experience. Do they have the equipment and workforce to handle your order size? Have they made similar products before? A factory visit, either by you or a trusted agent, is the best way to confirm their capabilities and see their operations up close.
Step 4: Share Product Designs and Specifications
Once you’ve selected a top candidate, it’s time to ensure they fully understand your product. This means sharing your complete product design files and detailed product specifications. This step is critical for moving forward to the sampling and prototyping phase.
Provide your manufacturer with everything they need to create an accurate sample. This includes 2D and 3D design files, the full spec sheet defining materials and colors, and any branding or packaging artwork. Clear and comprehensive information at this stage prevents costly errors later on.
This is also a good time to have an in-depth discussion about your expectations for the final product. Walk them through the design files and highlight any critical features or quality requirements. Make sure they confirm in writing that they understand all aspects of your product category before they begin making a sample.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Minimum Order Quantities
Negotiation is a key part of the sourcing process. Almost everything is negotiable, from price and payment terms to the MOQ. Approach negotiations with a collaborative mindset, aiming for a win-win outcome that builds a strong, long-term relationship with your supplier.
The MOQ is often a major point of negotiation, especially for new businesses. If the factory’s standard MOQ is too high for you, don’t be afraid to ask if they can be flexible. Many suppliers are willing to consider smaller orders, especially for a new client they hope to build a relationship with.
Here are a couple of strategies for negotiating a lower MOQ:
- Offer a higher price: A willingness to pay a premium per unit can convince a factory to accept a smaller order.
- Commit to future orders: If you can show a forecast for larger future orders, they may be willing to start with a smaller trial run.
Step 6: Request Samples and Evaluate Quality
Never, ever skip the sample stage. Before you commit to a full production run, you must get a physical sample of your product to inspect. This is your opportunity to evaluate the manufacturer’s work and check the product quality with your own hands.
When you receive the sample, scrutinize it carefully. Compare it against your spec sheet and design files. Does it meet all your requirements for materials, dimensions, colors, and functionality? Test it thoroughly to ensure it works as intended. This is your last chance to make changes before mass production begins.
If the sample isn’t perfect, provide clear and constructive feedback to the factory on what needs to be revised. It may take a few rounds of revisions to get the quality of products exactly right. Only approve the sample and move to mass production when you are 100% satisfied with the final version.
Step 7: Finalise the Order and Payment Terms
Once you’ve approved the final sample, it’s time to formalize the order. This involves signing a detailed purchase agreement or contract that outlines all terms of the deal. This legally binding document protects both you and the manufacturer and should leave no room for ambiguity.
Your contract should specify everything: the final product specifications, quality standards, order quantity, unit price, production lead time, and shipping details. It’s also crucial to clearly define the payment terms. The standard in China is typically a 30% upfront deposit to start production and the remaining 70% upon completion, before shipping.
Be sure to have a lawyer review the contract before you sign, especially one familiar with Chinese business law. This agreement will be your primary tool for recourse if any issues arise during the production process, so make sure it’s comprehensive and clear.
Step 8: Monitor Production Progress
Placing the order is not the end of your involvement. It’s important to monitor the production process to ensure everything stays on track. Don’t just wait for the factory to contact you with a completion date; be proactive and request regular updates.
Ask your supplier to send you photos and videos of the production line at various stages. This allows you to see the progress and spot any potential issues early on. Maintaining open and frequent communication throughout the whole process helps build trust and keeps your order top-of-mind for the factory.
This monitoring is a crucial part of managing your supply chain effectively. It helps you anticipate any potential delays and manage your timeline accordingly. If you’re working with a sourcing agent, they can visit the factory in person to check on the production process on your behalf.
Step 9: Arrange Quality Inspections
Do not rely solely on the factory’s internal quality control. You must have your own quality control procedures in place to verify the goods before they are shipped. The best practice is to arrange for an independent, third-party quality inspection.
These quality inspections should ideally happen at the factory before you make your final payment. An inspector will go to the factory and check a random sample of your products against a detailed checklist that you provide. This checklist should be based on your approved sample and quality standards.
An inspection report will alert you to any defects or deviations from your specifications. This allows you to address any issues of poor quality with the factory and have them corrected before the order leaves China. It’s a small investment that can save you from receiving a shipment of unsellable goods.
Step 10: Manage Shipping and Customs Procedures
Once your order has passed the final inspection and you’ve made the final payment, the last step is getting the products to their final destination. Managing shipping and customs procedures can be complex, so it’s often best to work with an experienced freight forwarder.
You have several shipping options, with the most common being sea freight and air freight. Sea freight is much cheaper but slower, taking several weeks. Air freight is significantly faster but also much more expensive. The right choice depends on your budget, timeline, and the size of your shipment.
Your freight forwarder will help you handle all the necessary paperwork for customs clearance in both China and your home country. They will ensure your shipment complies with all regulations, helping you avoid costly delays at the port. For businesses near the Greater Bay Area, shipping from major ports in Shenzhen or Hong Kong is common.
Protecting Your Intellectual Property in China
One of the most important aspects of custom manufacturing is protecting your intellectual property (IP). Your unique product design, brand name, and logo are valuable assets. It’s crucial to take proactive steps to safeguard them when working with manufacturers in China.
Ignoring IP protection can lead to your product specifications being copied or your trademarks being used by others without permission. Fortunately, there are effective legal tools, like NNN agreements and local registrations, that you can use to secure your IP. Let’s explore how to implement these protections.
Registering Trademarks and Patents
The single most important step you can take to protect your intellectual property in China is to register it there. China operates on a “first-to-file” patent and trademark system. This means that whoever files for the IP first owns the rights to it in China, regardless of who created it.
This is why you must register your trademarks and patents in China before you even begin discussions with manufacturers. If you don’t, you risk a “trademark squatter” registering your brand name and then holding it for ransom or selling counterfeit versions of your products legally within China.
The registration process can be complex, so it’s highly recommended to work with a law firm that specializes in Chinese IP law. They can help you navigate the system and ensure your applications are filed correctly, giving you the legal ownership you need to protect your product range and brand during the product development process.
Using NNN Agreements Effectively
A standard Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) from a Western country is often unenforceable in China. For real intellectual property protection, you need to use an NNN Agreement. NNN stands for Non-disclosure, Non-use, and Non-circumvention. This document is specifically designed for the Chinese legal system.
The “Non-use” clause prevents the factory from using your idea to produce their own products. The “Non-circumvention” clause stops them from bypassing you and selling your product directly to your customers. These additions provide much stronger protection than a simple NDA.
For an NNN agreement to be effective, it must be written in Chinese, governed by Chinese law, and be enforceable in a Chinese court. You should have every potential manufacturer sign this agreement before you share any confidential product specifications or details about your production process. It’s a critical tool for safeguarding your IP.
Safeguarding Product Designs and Molds
Beyond legal agreements, there are practical steps you can take to safeguard your product designs. When your product requires custom molds or tooling, it’s essential to have a clear agreement about who owns them. Your contract should explicitly state that you are the sole owner of any molds paid for by your company.
This prevents the factory from using your molds to produce extra units to sell on the side. Some businesses even arrange to have the molds shipped to them or a trusted third party after the production run is complete, giving them full physical control over these critical assets.
Ultimately, the best protection comes from working with a trusted and reputable manufacturer. Building a strong, long-term relationship based on mutual respect reduces the risk of IP theft. A good partner will be invested in your success and will work to protect your designs as part of the partnership, ensuring your final product remains exclusively yours.
Conclusion
Navigating the journey of custom product manufacturing can feel overwhelming, but it can also be rewarding with the right approach. Clear communication with your chosen Chinese manufacturers is key to ensuring product quality and meeting your specific requirements. Conducting thorough due diligence, exploring trade shows like the Canton Fair, and utilizing sourcing agents can enhance the entire process. Ultimately, creating high-quality products while managing production costs and maintaining quality control procedures will place your online business on solid ground. Embrace this adventure, and you’ll be well on your way to realizing your product visions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I ensure quality control with Chinese manufacturers?
To ensure quality control with Chinese manufacturers, establish clear communication about your standards, conduct regular inspections, and consider third-party quality assurance services. Utilize detailed contracts and maintain a close relationship for effective oversight throughout the production process.
What is a typical lead time for custom product manufacturing in China?
The typical lead time for custom product manufacturing in China ranges from 2 to 12 weeks, depending on factors like order complexity and production volume. It’s essential to communicate timelines with manufacturers to ensure timely delivery and meet your project deadlines.
How can I find reliable OEM China suppliers?
To find reliable OEM suppliers in China, utilize platforms like Alibaba and Global Sources. Research potential partners by checking reviews and ratings. Attend trade shows or use sourcing agents for better vetting. Ensure clear communication regarding quality standards and requirements throughout the process.
What steps should I take to protect my intellectual property?
To protect your intellectual property, register patents and trademarks, use non-disclosure agreements with partners, and monitor product usage. Additionally, consider legal advice to navigate laws in China, ensuring robust protection against potential infringements that could harm your business interests.